Finite element simulation for fluid mechanics
The work addresses the computational challenges of simulating magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flows, especially in nuclear fusion contexts where conductive fluids interact with strong magnetic fields. Such flows exhibit multiscale turbulence at high Reynolds numbers, complicating accurate heat transfer prediction. Traditional 3D simulations are computationally expensive, particularly with strong magnetic damping and complex geometries.
To tackle these challenges efficiently, the authors implement a projection-based variational multiscale (VMS) method under the quasi-two-dimensional SM82 approximation, significantly reducing computational cost.
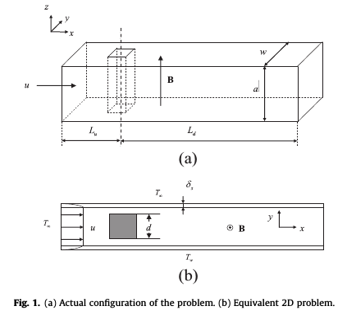
The VMS approach enables scale separation and stabilization without costly filtering, making it suitable for high Reynolds number MHD flows. This methodology balances accuracy with efficiency, showing potential for broader application in industrial MHD simulations.
…